Vietnam has become one of Asia’s most attractive destinations, welcoming millions of tourists and business travelers every year. Its unique culture, natural beauty, and economic opportunities have drawn people from all over the world. To manage this growing influx of visitors, the Vietnam visa policy has been designed to regulate entry, ensure security, and facilitate smooth travel experiences.
This article provides an in-depth explanation of the current visa policy in Vietnam, including who needs a visa, available visa types, exemptions, and how travelers can apply. It also highlights convenient services for those in urgent need of travel documents, ensuring a hassle-free journey.

Contents
What Is Vietnam Visa Policy?
Vietnam visa policy refers to the set of rules, regulations, and requirements established by the Vietnamese government to control the entry and stay of foreign nationals. It outlines which countries enjoy visa exemption, the types of visas available, application procedures, and conditions for extensions or renewals.
The policy is regularly updated to support tourism growth, foreign investment, and diplomatic relations. While some travelers enjoy visa-free entry, others must obtain visas before traveling or upon arrival at Vietnamese ports of entry.
Who Needs a Visa to Enter Vietnam?
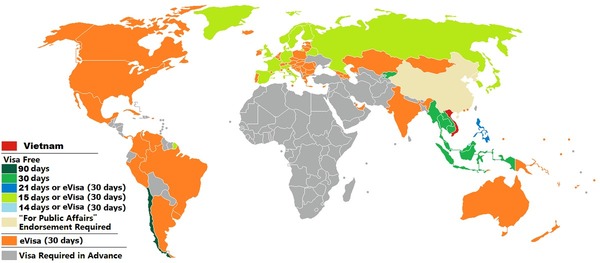
Not all travelers need a visa to visit Vietnam. Depending on nationality and purpose of visit, the requirements may differ:
- Visa exemption countries: Citizens from certain Southeast Asian and European countries can enter Vietnam without a visa for a limited period, usually between 14 to 45 days.
- E-visa eligible countries: Over 80 countries are eligible to apply for Vietnam’s electronic visa system, making the process simple and accessible online.
- Visa-required countries: Nationals from countries not listed under exemptions or e-visa categories must apply through an embassy or consulate before traveling.
Travelers should check the official updates frequently, as the visa policy can change depending on diplomatic agreements and government adjustments.
Types of Vietnam Visas
The Vietnam visa policy allows multiple types of visas tailored to the purpose of travel:
1. Tourist Visa
Issued to individuals visiting for leisure, sightseeing, or cultural exploration. This type typically allows a stay of 30 to 90 days, with single or multiple entry options.
2. Business Visa
For individuals attending meetings, conferences, or conducting trade activities. Business visas often have longer validity than tourist visas.
3. Student and Work Visas
Issued for academic or employment purposes. These require sponsorship from an institution or employer in Vietnam.
4. Diplomatic and Official Visas
Granted to foreign diplomats and government representatives with special conditions and exemptions.
5. Temporary Residence Cards
For long-term stays related to business or family purposes, usually valid for one to three years.
Vietnam Visa Exemptions
The Vietnam visa policy provides exemptions for specific travelers:
- Citizens of ASEAN nations such as Thailand, Malaysia, and Singapore enjoy visa-free entry for short visits.
- Nationals from select European countries, including Germany, France, and the UK, are exempt for up to 45 days.
- Special exemptions apply for diplomatic passport holders, official delegations, and APEC Business Travel Card members.
It’s essential for travelers to confirm their eligibility before planning their trips, as overstaying without a valid visa can result in penalties.
How to Apply for a Vietnam Visa
Travelers can choose different application methods depending on their nationality and travel urgency:
- E-visa: Applied online through the official Vietnamese government portal. This is one of the fastest and most convenient methods.
- Visa on Arrival (VOA): Available for travelers entering through international airports in Vietnam. Requires prior approval letters before departure.
- Embassy/Consulate application: Traditional method for those not eligible for e-visas or VOA.
Visa Extensions and Renewals
Foreigners already in Vietnam may extend or renew their visas if they need to stay longer. Extensions must be processed through immigration authorities before the existing visa expires. The procedure usually requires a sponsor, such as a company or travel agency.

Fast-Track Options for Travelers
Sometimes travelers need to enter Vietnam on short notice. In such cases, services like urgent visa to Vietnam help speed up the process, allowing applicants to obtain approval within hours. Similarly, rush Vietnam visa services are designed for last-minute travel plans, ensuring documents are processed in the quickest possible time.
For travelers who want professional assistance with urgent cases, Entry Vietnam Visa offers reliable support in securing expedited visas, helping visitors enter Vietnam smoothly and without stress.
Recent Updates in Vietnam Visa Policy
Vietnam has recently made efforts to simplify visa procedures and expand entry opportunities:
- Expansion of e-visa eligibility to more countries.
- Extension of visa-free stay for European travelers from 30 to 45 days.
- Streamlined processing systems to encourage tourism recovery post-pandemic.
- These changes reflect the government’s commitment to making Vietnam more accessible while maintaining border security.
The Vietnam visa policy provides flexible options for different categories of travelers while ensuring smooth entry and stay in the country. With multiple visa types, exemptions, and e-visa options, visitors can choose the most suitable path based on their travel purpose. For those in urgent need of a visa, fast-track services like urgent visa to Vietnam or rush Vietnam visa are available, offering peace of mind and efficiency.
For hassle-free applications, Entry Vietnam Visa is a trusted partner that helps travelers obtain visas quickly, including expedited cases. By understanding the policy and planning ahead, international visitors can enjoy Vietnam’s vibrant culture, breathtaking landscapes, and dynamic economy without unnecessary delays.



